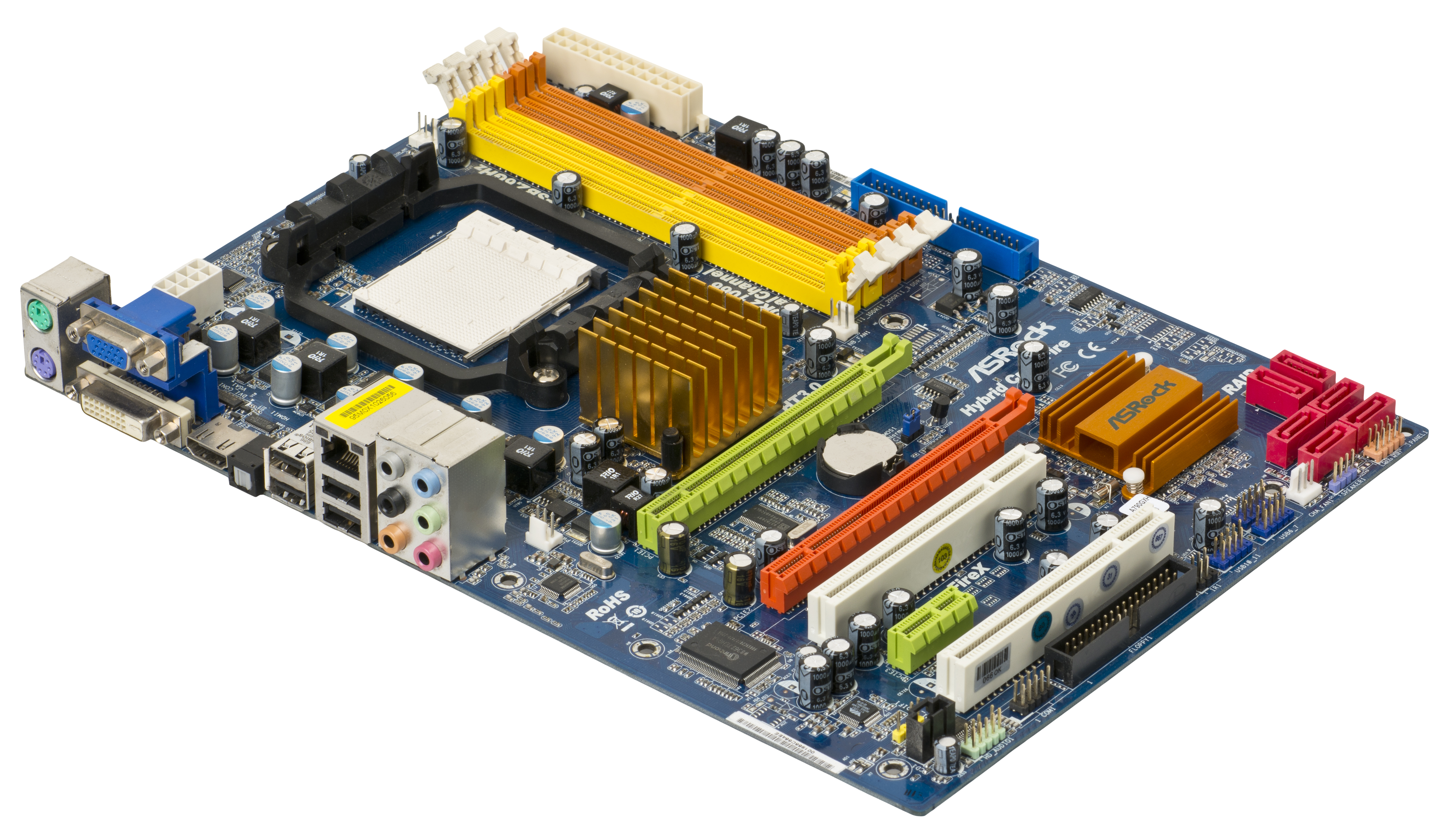
The Motherboard
The motherboard acts as the central coordination point for a computer, enabling the various components to work together efficiently. It is often considered the "nervous system" of the computer, facilitating communication and ensuring that the computer functions as a cohesive unit.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is often referred to as the "brain" of a computer, and its primary purpose is to execute instructions and perform various tasks that are essential for the computer's operation. The CPU carries out a wide range of functions, including:
Connectivity:
The motherboard provides physical connectors and pathways for all major computer components to communicate with each other. It links the CPU, RAM, storage devices, graphics card, and various peripherals.
Data Transfer:
It manages data transfer between components, ensuring that information flows seamlessly between the CPU, RAM, and other parts.
Power Distribution:
The motherboard distributes power to all connected components, ensuring they receive the correct voltages and currents to operate effectively.
BIOS/UEFI:
It houses the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), which is responsible for booting the computer, initializing hardware, and controlling essential system settings.
Clock Generation:
The motherboard generates the system clock signal that synchronizes the timing of operations within the computer.
Peripheral Connectivity:
It provides connectors for external devices like USB ports, audio jacks, networking ports, and expansion slots for adding additional components.
Expansion:
The motherboard often includes slots for adding expansion cards, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network adapters.
Memory Support:
It has slots for installing RAM (Random Access Memory), allowing the computer to access and work with data quickly.
Form Factor:
Motherboards come in various sizes and shapes, known as form factors, which determine the physical dimensions and the types of components that can be installed. Common form factors include ATX, microATX, and mini-ITX.
Compatibility:
The motherboard's chipset and socket type must match the CPU you intend to use, ensuring compatibility between the central processing unit and the motherboard.