Atoms and Emission Lines
|
An atom is made up of three main components: protons, neutrons (found in the nucleus)
and electrons. In a neutral atom (without charge), the number of protons (positive charge)
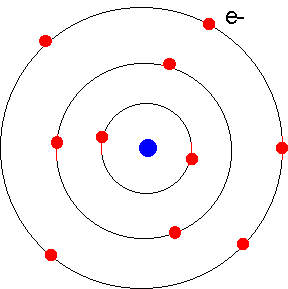
and electrons (negative charge) are equal. To the right is a highly simplified diagram of an atom. The important point is that the electrons reside in specific orbits, which circle around the central nucleus of protons and neutrons (shown here as a single blue dot). These orbits correspond to specific energies. |
|
|
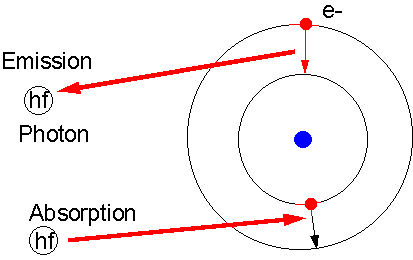
In order for an electron to move
up (out), it must gain energy. When an electron moves down (in), it gives up
the energy difference. This energy difference is given up (released) or obtained (absorbed) through photons of light which have the exact same energy as the orbital energy difference. |
|
