Calibration
For the rest of the experiments that will be performed in this course, a sophisticated microprocessor controlled HP-8510 vector network analyzer with which precision microwave measurements can be made will be used. Please follow the instructions carefully. Every partner should repeat the calibration procedures.- Turn on the system in the following order: (Please refer to Network Analyzer Manual)
- Source (HP-8550B)
- Test set (HP-8515A)
- System peripherals (if used) plotter, printer, etc.
- Network analyzer (8510A)
- The network analyzer goes through out initiation and self-test. Once this is complete, press PRESET.
- Set Stimulus, Format and Response function blocks to your requirements. Familiarize yourself with these settings. Follow the sequences on the attached sheets.
- Calibrate the Network Analyzer for single port and then make the following measurements.
Experiments
- Load measurements.
Using the network analyzer, measure the loads that you have used in Experiments #1 at higher frequencies and observe the changes in load impedance values. - Cavity Q measurements.
- Measure the resonant frequencies and the Q of the cylindrical cavity up to 15.0 GHz.
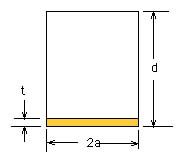
- From the dimensions of the cavity (2a=18.0 mm and d=29.0 mm) find the theoretical modes that correspond to the experimentally measured resonant frequencies.
- Cavity perturbation.
Pick one of the lowest resonant modes of the cavity. Cut a very thin plastic sheet (thickness lot thinner than d) to a circular shape with a diameter equal to the diameter of the cylindrical cavity. Insert the plastic sheet into the cavity. Measure the shift in resonant frequency and change in Q of the cavity to observe the effects of the material perturbation of the cavity. This technique is used as a means to measure the dielectric constant and loss tangent of a dielectric material.
 Refer to Pozar, Section 6.8 (p.340) for the theory. Can you find the dielectric constant by following the theory given in the book? (extra credit)
Refer to Pozar, Section 6.8 (p.340) for the theory. Can you find the dielectric constant by following the theory given in the book? (extra credit)
Goto Homepage