

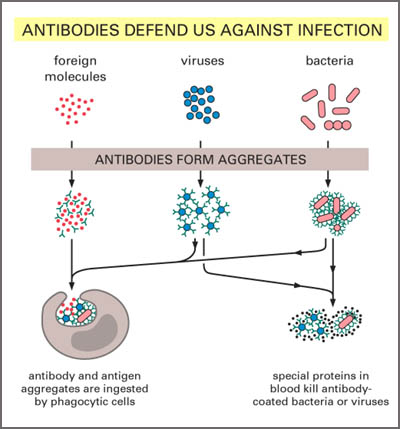
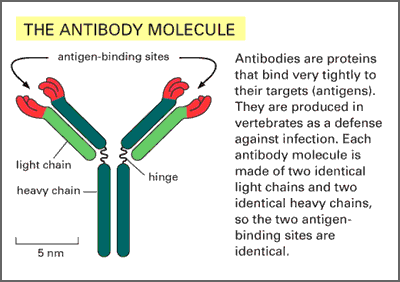
The typical antibody molecule, shown above (1) and below (2), is made up of four polypeptide chains, comprising of two identical light chains and two identical heavy chains.
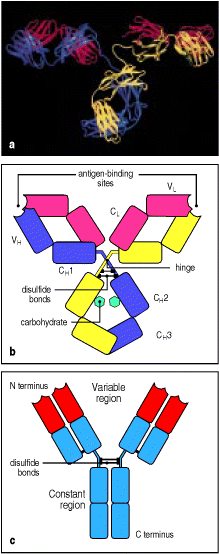
Each of the four chains has a variable (V) region at its amino terminal end which contributes to the specificity at the antigen-binding site (1).
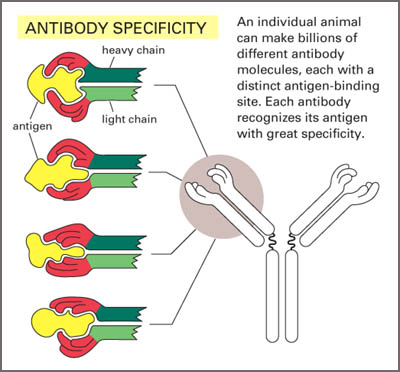
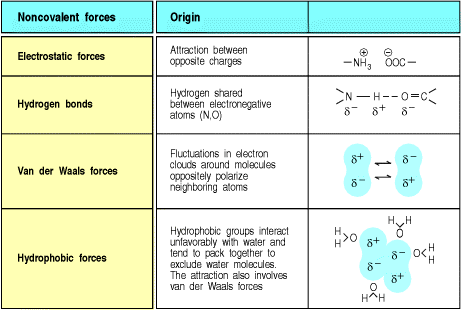
Electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic interactions can all contribute to the antibody-antigen binding specificity and affinity (2).
References:
1. http://www.accessexcellence.org/AB/GG/antibodies.html
2. Janeway CA, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik M. 2001. Immunology, 5thed. New York: Garland Publishing. p95-102.