

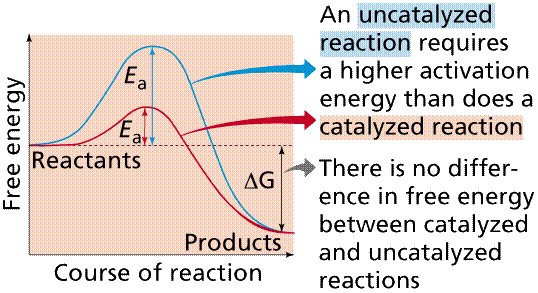
Enzymes allow many chemical reactions to occur within the homeostasis constraints of a living system. Enzymes function as organic catalysts. A catalyst is a chemical involved in, but not changed by, a chemical reaction. Many enzymes function by lowering the activation energy of reactions. By bringing the reactants closer together, chemical bonds may be weakened and reactions will proceed faster than without the catalyst. (1)
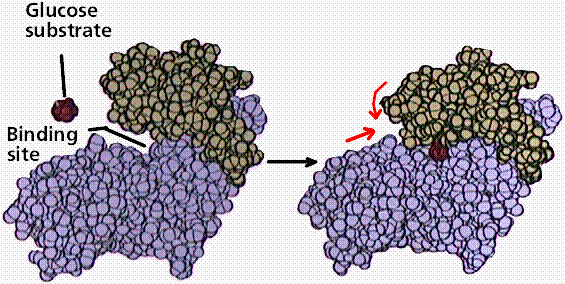
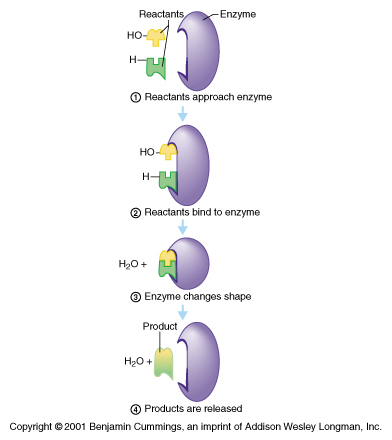
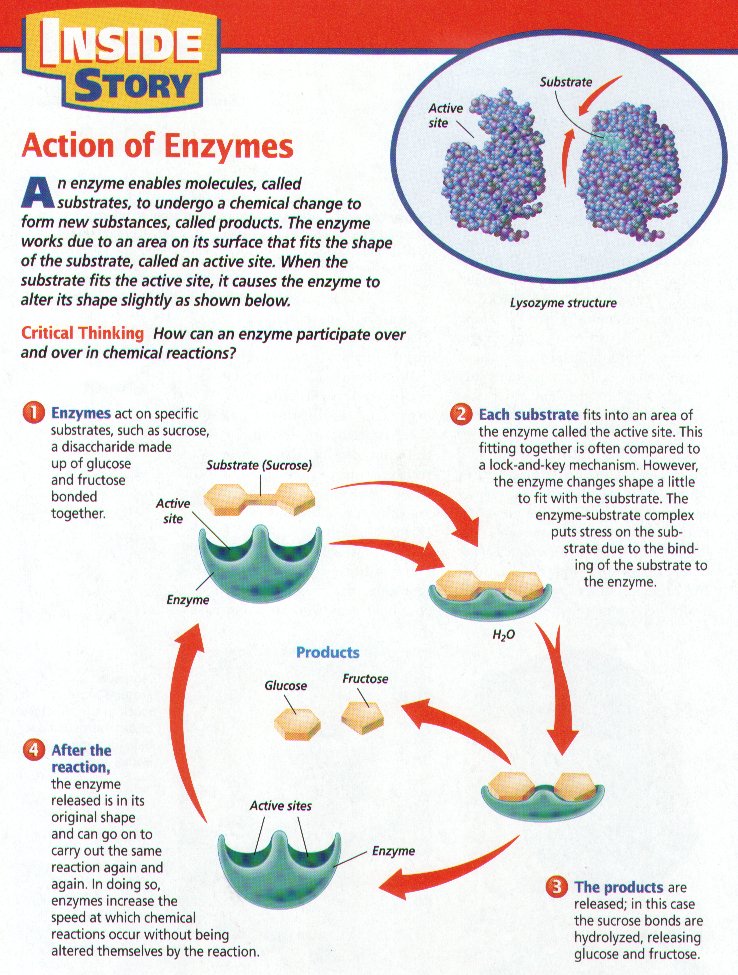
Enzymes are proteins. The functioning of the enzyme is determined by the shape of the protein. The arrangement of molecules on the enzyme produces an area known as the active site within which the specific substrate(s) will "fit". It recognizes, confines, and orients the substrate in a particular direction as seen in the following diagrams. (1,2)
References:
1.http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookEnzym.html
2. http://www.bmb.psu.edu/courses/bisci004a/chem/basechem.htm
3. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/enzymes.html