| A. increase total real output while reducing the price level.
B. shift aggregate demand to the classical range of the supply curve. C. shift the aggregate supply curve to the left. D. increase taxes to finance increased government expenditures on public works projects such as highways and mass transit. E. supplement increased government spending with increased consumer spending on goods and services. |
50. In the video Nariman Behravesh argued that the supply-side impact
of the
Reagan tax cuts was
| A. very large, leading to increased government tax revenues.
B. about equal in magnitude to the demand side impact of those cuts. C. enough to ensure that the size of the federal budget deficit would decrease. D. small at first, but likely to grow as time went on. E. virtually nonexistent, although they did boost investment and lead to higher productivity. |
51. In the video Edwin Mansfield notes that one reason why R & D
spending by firms has declined as a percent of national output is that
| A. there is very little left to invent since research was so great
in the first half of the twentieth century.
B. most research goes to enhance military spending which is no longer as important as it once was. C. a firm cannot appropriate all of the benefits it creates from R & D because they spill over to outsiders so it tends to underinvest in this area. D. R & D rarely results in marketable products so increasingly it is being performed in government research facilities. E. stagflation has made R & D unprofitable for the smaller firms that carry out the largest share of this activity. |
52. The difference between the budget deficit and the national debt
is that the deficit is
| A. financed by borrowing; the debt by selling bonds.
B. a long-term concept; the debt, a short-term concept. C. the difference between the size of the debt and the amount of government revenues in a given year. D. the amount the government must raise to create full employment. E. the difference between expenditures and revenues; the debt, the total amount owed by the government. |
53. Which of the following countries has the most burdensome budget
deficit?
| GDP | Government budget deficit | |
| Country A | $ 100 billion | $ 2 billion |
| Country B | $ 300 billion | $ 35 billion |
| Country C | $1,000 billion | $ 50 billion |
| Country D | $2,500 billion | $100 billion |
| Country E | $4,500 billion | $250 billion |
| A. Country A
B. Country B C. Country C D. Country D E. Country E |
54. A budget deficit will have its inflationary impact reduced by
| A. borrowing from the public.
B. creating new money. C. borrowing from the central bank. D. simultaneously reducing taxes. E. raising the national debt. |
55. If people believe that in the future the government will have to
resort to creating money in order to pay the interest on debt, which is
being currently financed by the sale of bonds, they may
| A. try to hold less money now, pushing up the current demand for goods
and services as well as the current price level.
B. increase the demand for current government bonds, raising bond prices and reducing interest rates. C. reduce current consumption because they expect price levels to fall in the future as the government is forced to lower taxes. D. increase their current holdings of government bonds because they expect interest rates on government bonds to rise. E. do any of the above since government deficits have an unpredictable impact on the economy. |
56. The crowding-out effect
| A. is a basic tenet of Keynesian analysis.
B. occurs when people expect prices to rise as a result of stabilization policy and take measures to raise their wages. C. asserts that expansionary fiscal policy will bid up interest rates and reduce private spending. D. asserts that an increase in aggregate supply will force down price levels and reduce competition for output by households and businesses. E. states that increasing the money supply will lower interest rates, making it impossible for some borrowers to obtain adequate funds. |
The question(s) below are based on the following diagram:
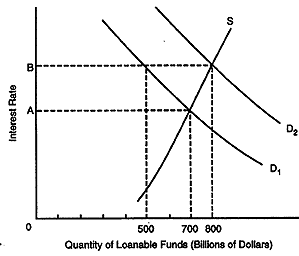
57. If S is the supply curve of loanable funds, D1 is the demand curve
for loanable funds before government borrowing, D2 is the demand curve
for loanable funds after government borrowing, the size of the government
deficit must be
| A. $800 billion.
B. $700 billion. C. $500 billion. D. $300 billion. E. $100 billion. |
58. As a result of government borrowing, private sector borrowing is
| A. unaffected.
B. reduced by $100 billion. C. reduced by $200 billion. D. reduced by $300 billion. E. reduced by $500 billion. |
59. The idea that an economy experiencing considerable unemployment
and government deficit spending may increase output, which in turn may
increase investment, is called the crowding-
| A. out effect.
B. through effect. C. over effect. D. in effect. E. under effect. |
60. Balancing the government’s budget each and every year
| A. is necessary because all debts eventually come due.
B. is a fundamental tenet of Keynesian economics. C. is sensible for the same reasons as is balancing the family budget. D. makes it difficult to use fiscal policy to stabilize the economy. E. will result in simultaneous inflation and unemployment. |
61. A budget policy in which the government is expected to run a big
enough surplus during periods of high employment to offset deficits during
an ensuing period of excessive unemployment is called
| A. an annually balanced budget.
B. a structural budget. C. a full-employment budget. D. a conflict-resolution budget. E. a budget balanced over the course of the business cycle. |
62. The U.S. government’s fiscal year runs from
| A. January 1 to December 31.
B. April 15 to April 14. C. June 1 to May 31. D. October 1 to September 30. E. December 1 to November 30. |
63. The Senate committee that considers major tax legislation before
it goes to the entire Senate is called the
| A. Ways and Means Committee.
B. Finance Committee. C. Tax Analysis Committee. D. Tax Legislation Committee. E. Senate Budget Committee. |
64. Supply siders argue that the current federal budget surpluses should
be used to
| A. pay down the national debt.
B. increase government spending on education and health care. C. finance tax reductions. D. eliminate the deficit in the balance of payments. E. increase the money supply. |
65. Our money has value because
| A. it is backed by gold.
B. its supply is unlimited. C. it is guaranteed by banks. D. people will accept it in payment for goods and services. E. it is the result of public and private debt. |