
ffff ffff ffff 00b0 d083 9782 0806 0001 0800 0604 0001 00b0 d083 9782 c0a8 0169 0000 0000 0000 c0a8 0101 00b0 d083 9782 0060 9796 a33f 0806 0001 0800 0604 0002 0060 9796 a33f c0a8 0101 00b0 d083 9782 c0a8 0169 0060 9796 a33f 00b0 d083 9782 0800 4500 0054 0000 4000 4001 2d31 c0a8 0169 0ae4 4083 0800 189c 9001 0000 72fe 1c42 88df 0d00 0001 0203 0405 0607 0809 0a0b 0c0d 0e0f 1011 00b0 d083 9782 0060 9796 a33f 0800 4500 0054 bb49 0000 3f01 b2e7 0ae4 4083 c0a8 0169 0000 209c 9001 0000 72fe 1c42 88df 0d00 0001 0203 0405 0607 0809 0a0b 0c0d 0e0f 1011Notes:
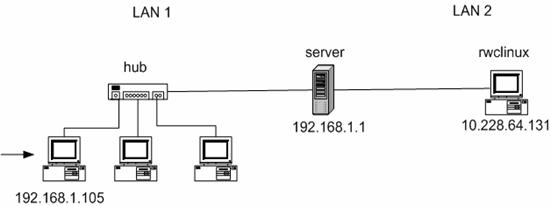
a. the machine with hostname “server” acts as a router
b. all padding and trailers have been ommited
Using the diagram and the 4 packets on the previous page, answer and understand the following (note the initiator of this sequence is indicated by the arrow):