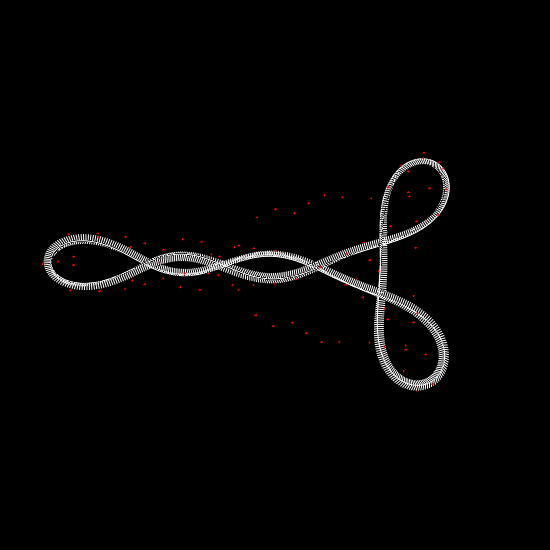
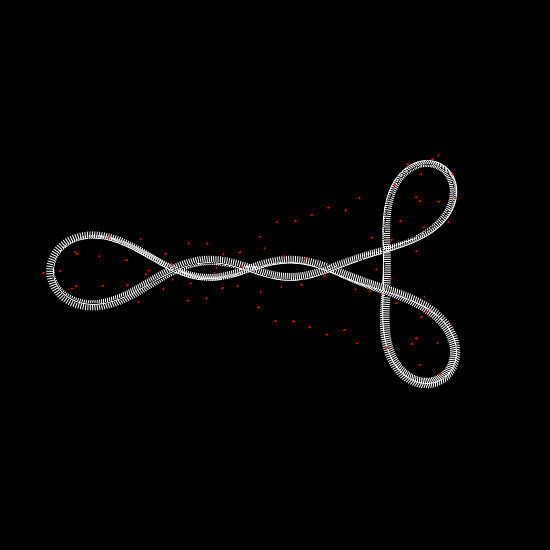
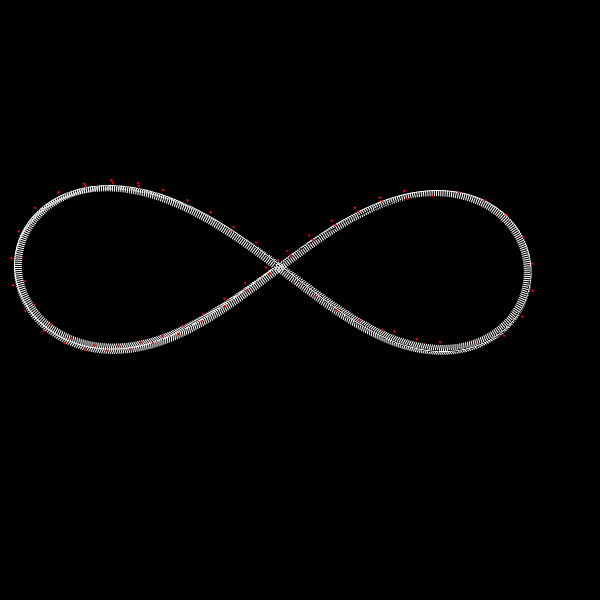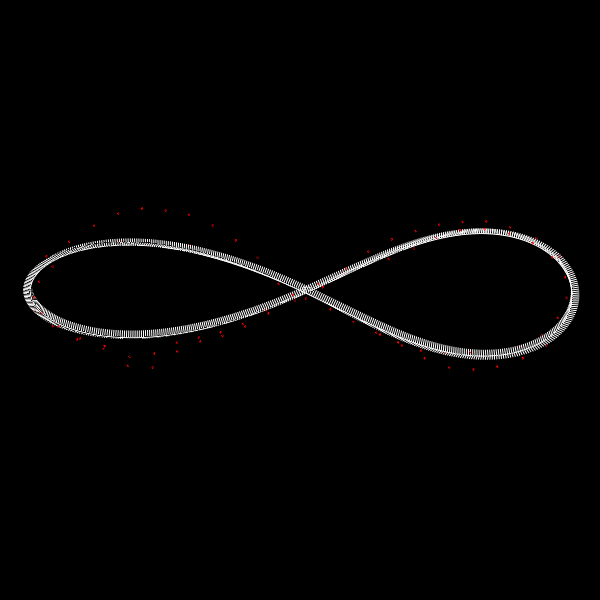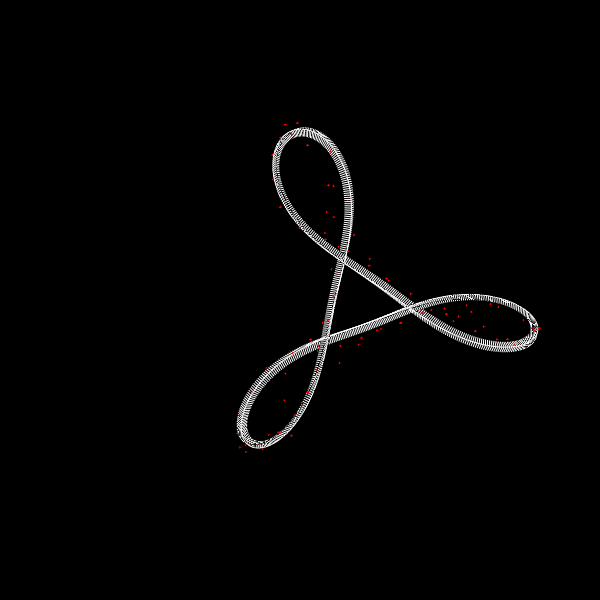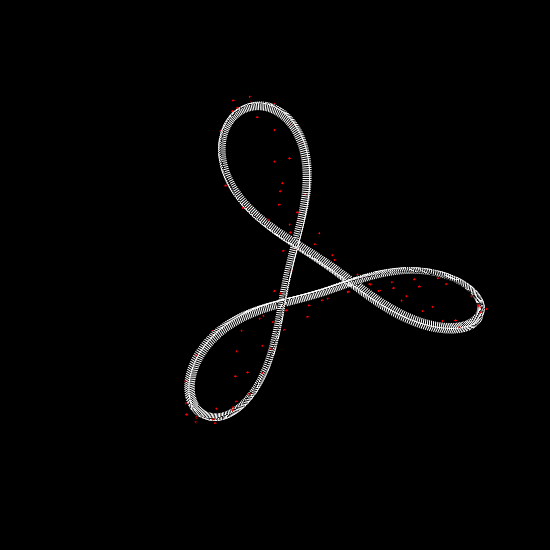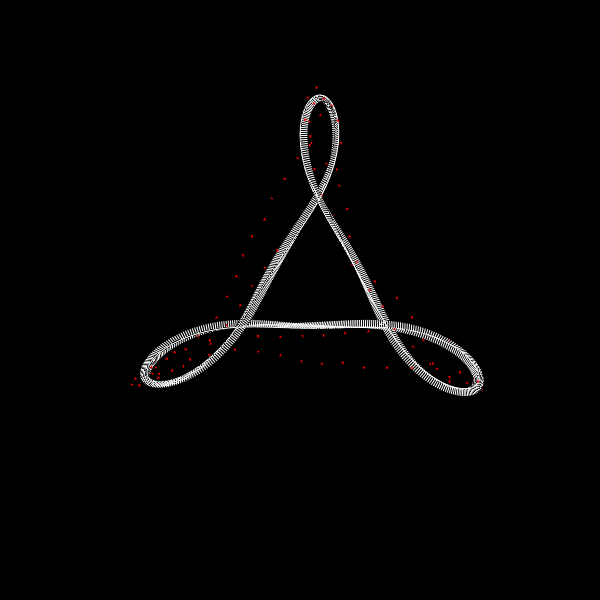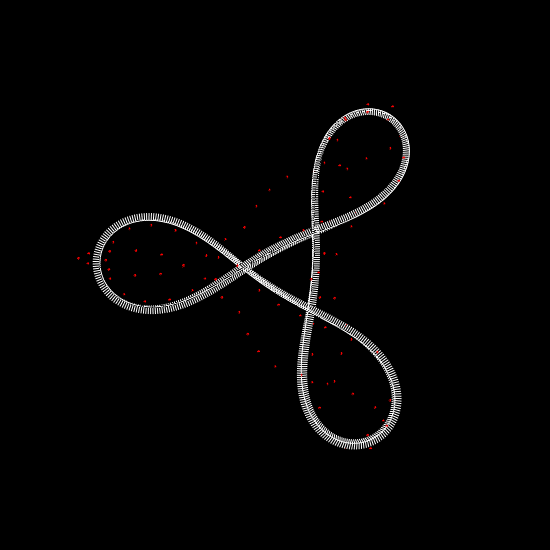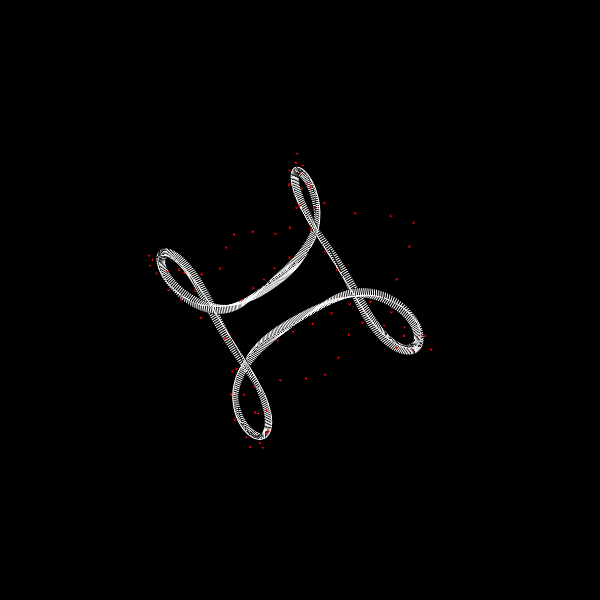Deformation of a circular DNA in fluid
|
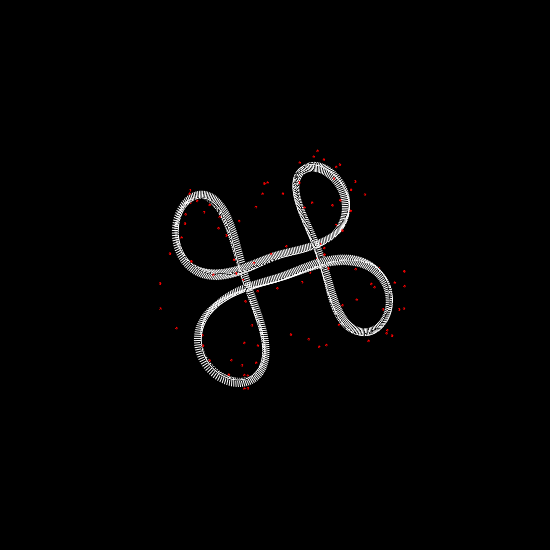
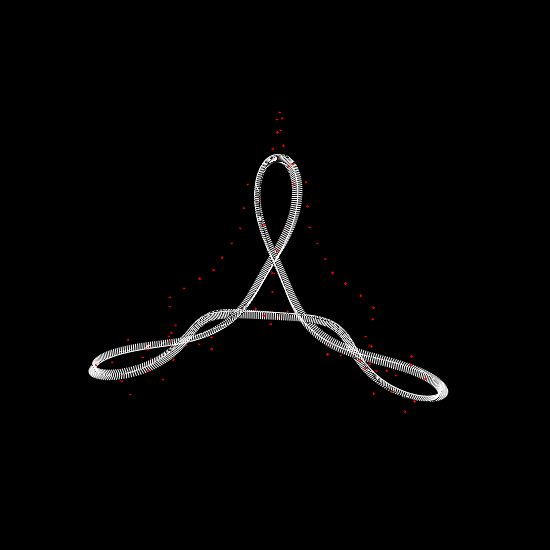
We investigate the effects of electrostatic and steric repulsion on the dynamics of pre-twisted charged elastic rod immersed in a viscous incompressible fluid. Equations of motion of the rod include the fluid-structure interaction, rod elasticity, and a combination of two interactions that prevent self-contact, namely the electrostatic interaction and hard-core repulsion. The governing equations are solved using the generalized immersed boundary method. We find that after perturbation, a pre-twisted minicircle collapses into a compact supercoiled configuration. The collapse proceeds along a complex trajectory that may pass near several unstable equilibrium configurations, before it settles in a locally stable equilibrium. The dwell time near an unstable equilibrium can be up to several microseconds. Both the final configuration and the transition path are sensitive to the initial excess link, ionic strength of the solvent, and the initial perturbation. References:S. Lim, Y. Kim, and D. Swigon, Dynamics of an electrostatically charged elastic rod in fluid, Proc. R. Soc. A (2010) |
|
|
|||
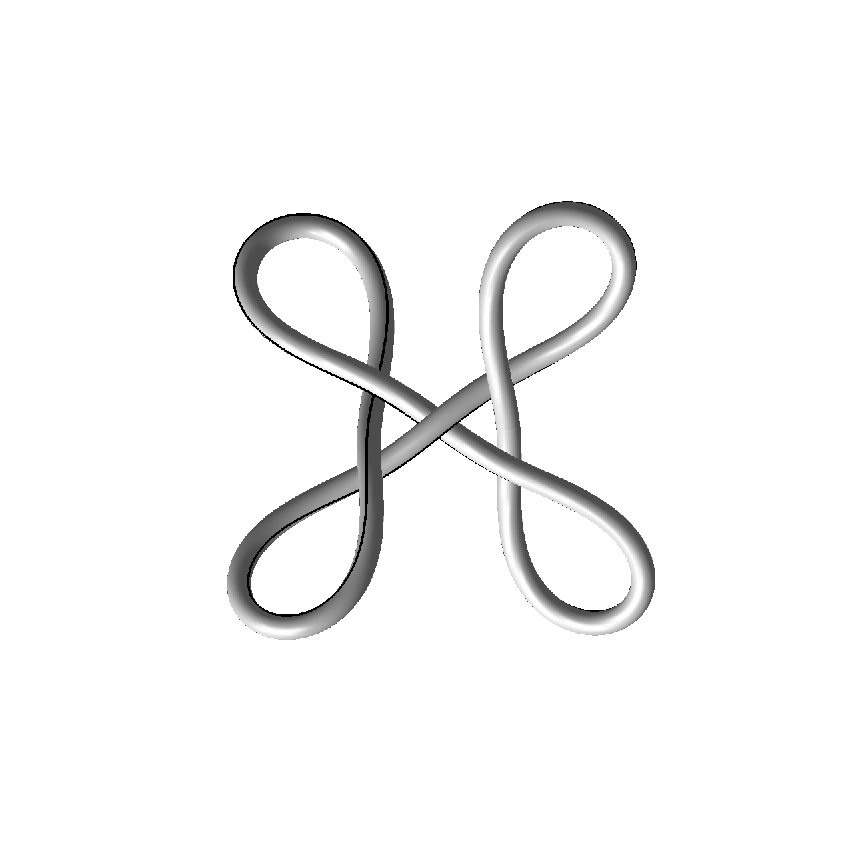 |
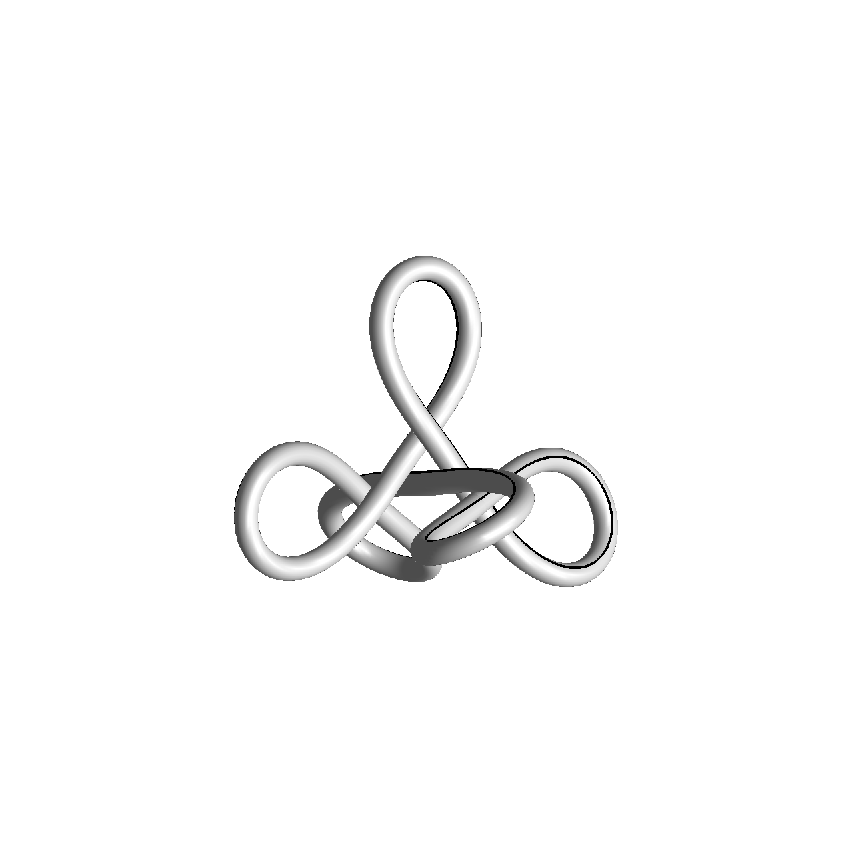 |
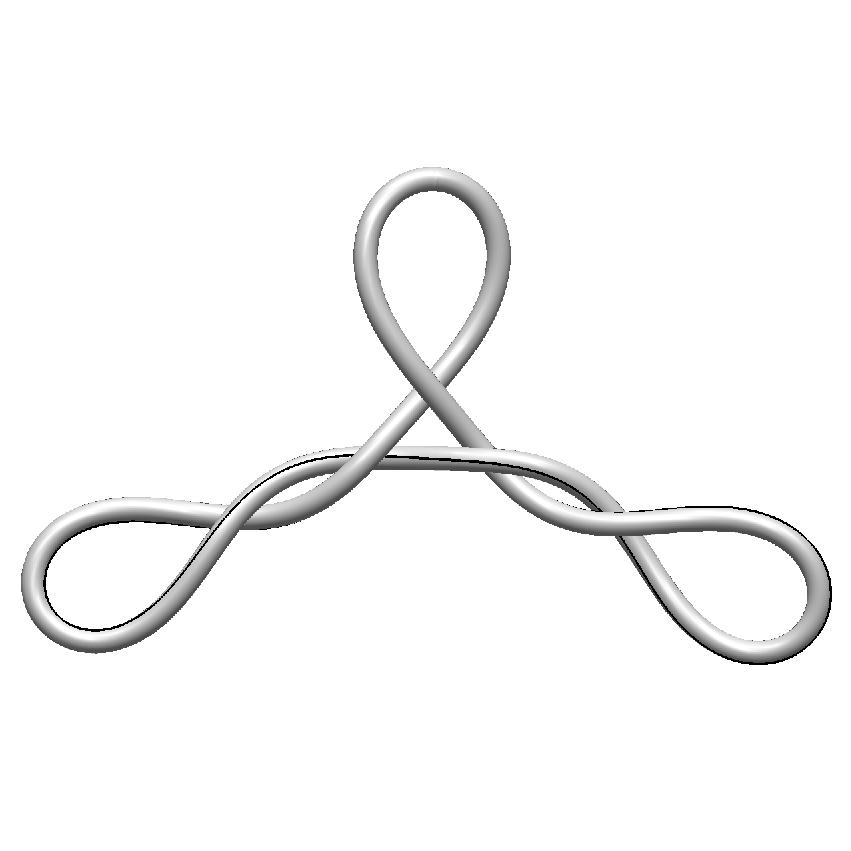 |
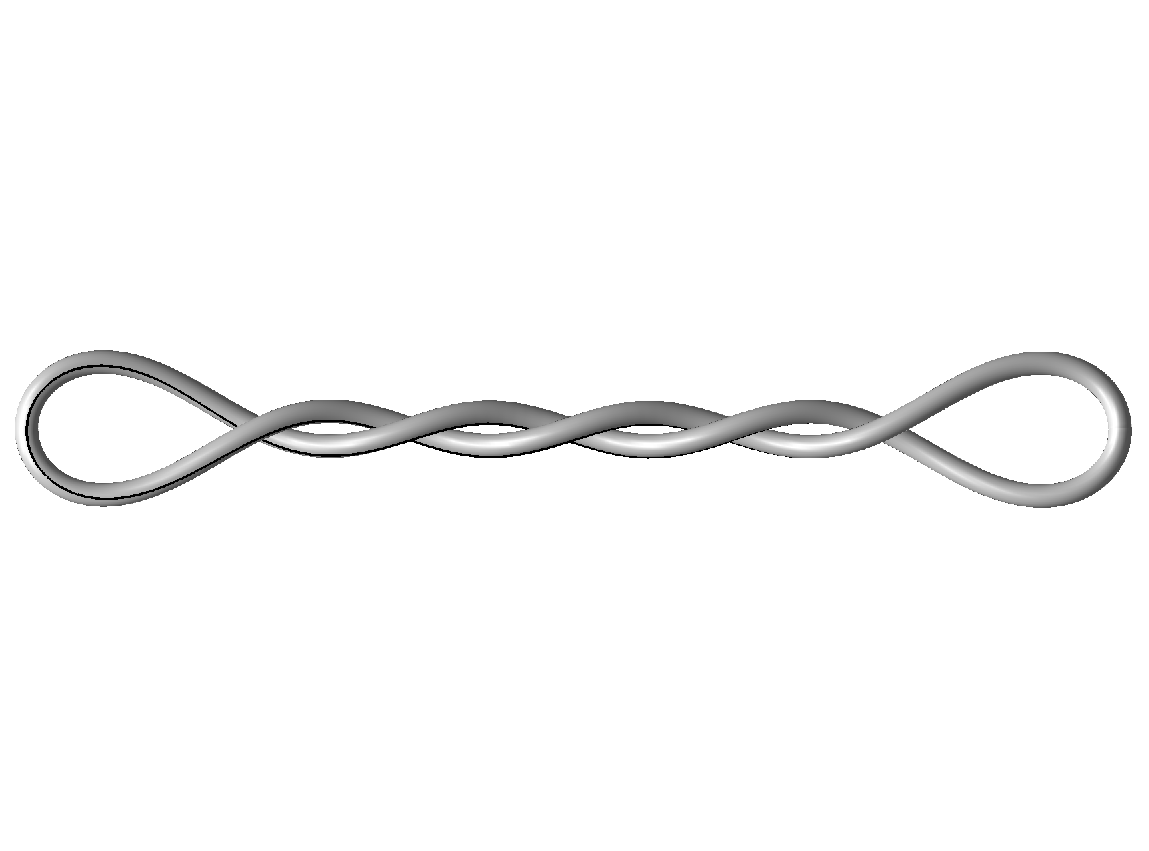 |
z0p01p3.tar.gz
z0p1p5.tar.gz