Problem Set 2
Problem 6
E773 Apparatus
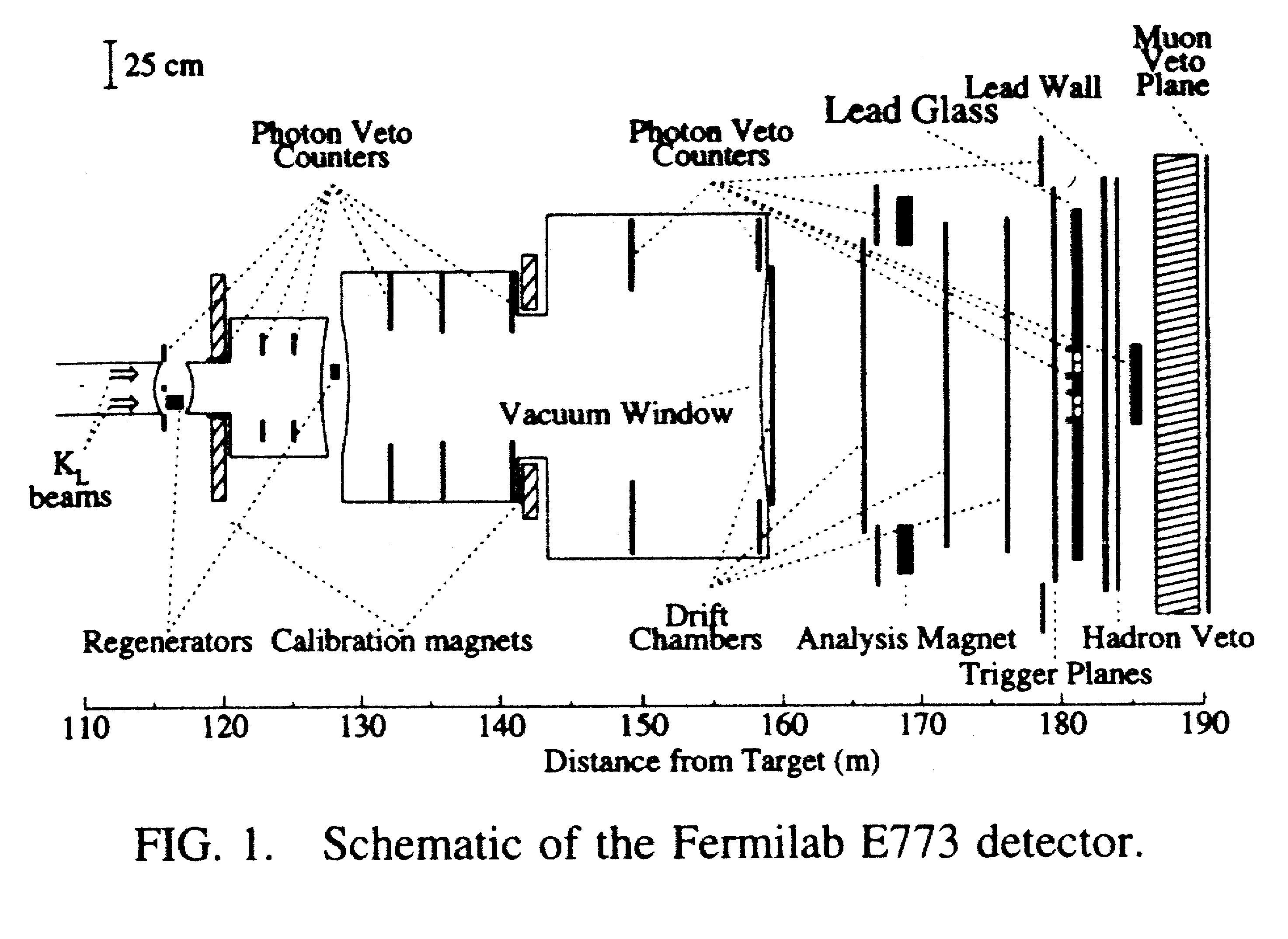
Part A - Identification of primary reaction
Charged particle decay mode
The drift chambers measure the positions of the two charged particles after
the vacuum window. These particles are bent by the analysis magnet. Thus
with a combination of the drift chambers and the analysis magnet, the initial
angles of the pions and their momenta are measured. From these the initial
decay position and the mass of the parent particle is determined.
Neutral decay
The positions and energies of the photons coming from the pi-zero decays
are measured in the lead glass. If you assume that you know which two of
the four photons come from each pion, you can use the constraint of the
pion mass to determine how far upstream each pion was produced. From this
distance and the energies and positions of the photons at the lead glass,
you can determine the mass of the parent particle.
Part B -- Rejection of background
Three pion decays
Each of the three pion decays has an extra pi-zero which would lead to
two extra photons in the final state. These extra photons would be seen
as either extra showers in the lead glass or as extra hits in the photon
veto counters. In addition, the extra pi-zero takes away energy from the
final state. If the mass of the initial state is calculated from the two
remaining pions, it would be lower than the kaon mass.
K-mu 3 Decay
The muon in the final state is a penetrating particle and would penetrate
the hadron veto and appear in the muon veto plane. Any events with hits
in this plane are rejected. Finally, the anti-neutrino takes away energy
from the reaction. As a result, the reconstructed mass from of the pion-muon
system would be less than the kaon mass.
