-
In a MATHEMATICAL sense, Wien's Law looks like this:
- What is the temperature of your stove, if you can see it glowing at very, very red wavelengths (about 0.9 microns)? And do you really think its that hot?
- What is the peak wavelength emitted by Rigel, a Blue Super-giant Star in Orion, with a T(K) is about 15,000 K?
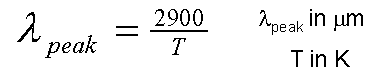
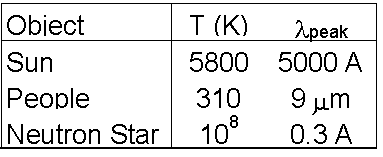
We apply this to a few ordinary objects. For instance, the wavelength the sun most strongly peaks at is in the optical, at around 5000 A. People however, are much colder. Most of our thermal radiation is emitted as infrared radiation. Neutron Stars are strong X-ray emitters because they have extremely high temperatures.
A few example calculations: