| Kepler's Second Law:
II. The line joining the planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in
equal times as the planet travels around the ellipse.
|
 |
| Kepler's Third Law:
III. The ratio of the squares of the revolutionary periods for two
planets is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their semi-major axes:
|
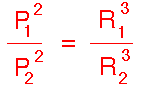 |
Calculations using Kepler's Third Law
A convenient measurement for periods is
Earth years. A convenient measurement
for distances is the average separation of the Earth
from the Sun, an astronomical unit (AU). If
these units are used in Kepler's 3rd Law, the
denominators in the preceding equation equal "1" (assume
Planet "2" is Earth, with distance = 1 AU, period = 1 year)
and it may be written in the simple form:
With a bit of algebra, it can be expressed in years or distance:
To calculate the "radius" of Mars orbit (semi-major axis) from the orbital period: Mars orbits the Sun in 1.88 Earth years: