What Can DNA Tell us About Life?
Bacteria
Archaea
The Eurkaryota
Viruses
The Theory.
By comparing DNA sequences, three specific Domains of Life
have been identified. These are The Prokaryotes: Bacteria and Archaea, and The Eukaryotas.
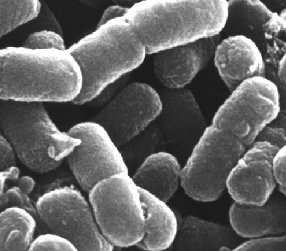
Bacteria are of immense importance because of their
flexibility, capacity for rapid growth and reproduction,
and great age - 3.5 billion year old fossils contain bacteria-like organisms.
Bacteria are often maligned as the causes of human and
animal disease. However, certain bacteria produce antibiotics
such as streptomycin.
 Only quite recently have these organisms been identified as a
major domain of life. They don't look much different from
Bacteria, however, biochemically and genetically, they are
as different from bacteria as you or I. They include
inhabitants of some of the most extreme environments on
the planet.
Only quite recently have these organisms been identified as a
major domain of life. They don't look much different from
Bacteria, however, biochemically and genetically, they are
as different from bacteria as you or I. They include
inhabitants of some of the most extreme environments on
the planet.
Eukaryota include the organisms that people are most familiar
with - all animals, plants, and fungi. They share fundamental
characteristics of cellular organization, biochemistry,
and molecular biology.
They are not like eukaryotes, archaeans, or bacteria
because they depend on their host cells to reproduce.
However, they are of considerable biological importance. Viruses
cause a number of diseases in animals (smallpox, the
common cold, chickenpox, influenza, shingles, herpes, polio, rabies,
Ebola and AIDS). Different strains infect other organisms such
as plants, bacteria and archaea.