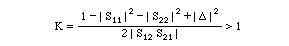Stability Test.
- Using the S parameters of the transistor, calculate
- the stability factor K
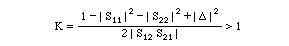
and
- D= S11S22-S12S21
If K > 1.0 and D < 1.0, then the transistor is Unconditionally Stable, You can use Simultaneous Complex Conjugate Match.
If K < 1.0, then the transistor is Conditionally Stable.
Proceed with Stability Circles to find out stable regions of operation.
Unconditionally Stable:
The transistor is unconditionally stable means that any arbitrary source and any arbitrary load impedance can be connected at the input and output terminals of the transistor and the transistor operation will be stable at that frequency and bias conditions.
Conditionally Stable:
The transistor is conditionally stable means that all arbitrary source and load impedance can not be connected at the input and output terminals of the transistor. At that frequency and bias conditions, the transitor operation will be stable only for a range of input and/or output impedances connected at the input and output terminals of the transistor. For other impedance values, the transistor operation will be unstable