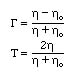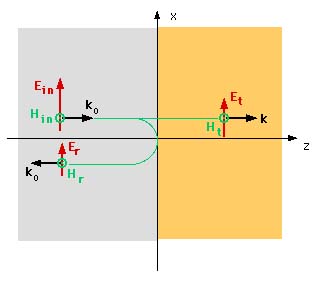
A plane wave is incident from -oo on a dielectric interface at z=0. The dielectric occupies the space from 0 to oo and extends in all x and y directions as shown in the figure below. The material properties are (m, e). The region -oo to 0 in the z direction is the free space.

From the properties of the plane waves, the incident fields can be written as
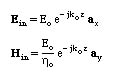
The reflected fields can be written as
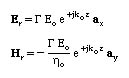
Here G is defined as the reflection coefficient and is equal to G=Er /Ein.
And finally, the transmitted fields can be written as
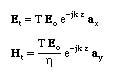
Here T is defined as the transmission coefficient and is equal to T=Et /Ein.
Applying the boundary conditions on the tangential components of the total E field at the boundary (i.e. at z=0), we obtain
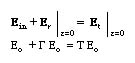
Applying the boundary conditions on the tangential components of the total H field at the boundary (i.e. at z=0), we obtain
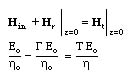
Solving these two equations for G and T, we find