University of Cincinnati--ECE&CS Department
Reflection of a Plane Wave from a Good Conductor (Metal)
Prepared by: Prof.Altan M. Ferendeci
Assume a plane wave is incident from -oo on conductor loacted at z=0. The direction of propogation is in the +z direction and the the propogation vector is normal to the conductor surface. The metal extends all over in the (x,y) plane and all the way into z=+oo.
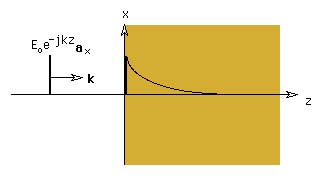
By inspection, we can write the total fields in the free space (incident plus reflected) as:
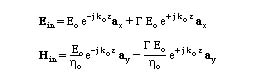
The fields in the metal (from the above solution) are
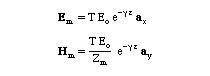
applying the continuity of the tangential E and H fields (assuming there are no surface charges at the interface)
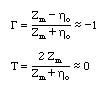
We conclude that almost no field is transmitted into the conductor and all the incident field is compeletely reflected back.
We can study the fields in the free space by substituting G=-1 into the above E and H fields and evaulte the time dependent E and H fields. For the E field
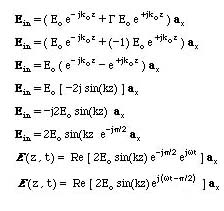
and for the H field
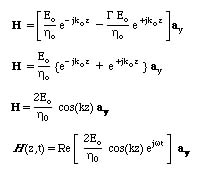
These are called standing waves.
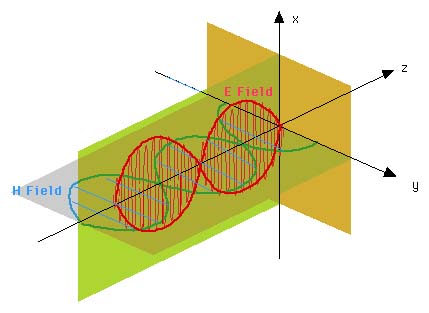 Click image for a bigger picture
Click image for a bigger picture
The results can be summarized as
- Each field goes through zero every lo/2
- The time phase difference beween the E and H fields is p/2
- E is zero H is a maximum at the condcutor interface and
- When H is zero, E is a maximum and vise-versa
.
Back to Micro. Comm
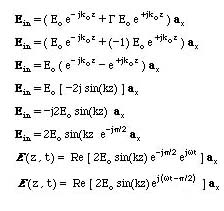
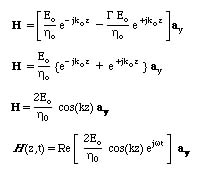
 Click image for a bigger picture
Click image for a bigger picture
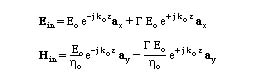
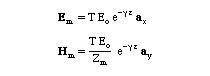
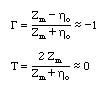
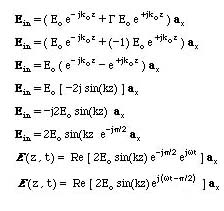
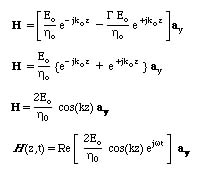
 Click image for a bigger picture
Click image for a bigger picture