All About the Ocean
Home
Summary
Hello! Welcome to "All About the Ocean." This is a resource where you can explore various aspects related to the ocean. We dive into the workings of the ocean, the diverse marine life it houses, and the issue of pollution in and around these waters. As you navigate through this site, you have the option to read summaries on this page or click on the titles for more in-depth information. If you choose the more in-depth route, you'll find a navigation button at the bottom of each page, making it easy to switch between topics seamlessly. This site is here to provide you with a wealth of knowledge. Dive in and explore the wonders of the oceanic world!
Ocean
The ocean is a vast body of water that covers more than 70% of the Earth's surface. It plays a crucial role in regulating the planet's climate, absorbing a significant portion of carbon dioxide and heat. The ocean is divided into different zones, including the sunlit surface zone, the twilight zone, and the dark abyssal zone. It supports a diverse array of life forms, from microscopic plankton to large marine mammals. The ocean also sustains numerous ecosystems such as coral reefs, kelp forests, and deep-sea hydrothermal vents, providing essential resources and habitats for countless species. However, it faces various threats, including pollution, overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change, which significantly impact its health and biodiversity.

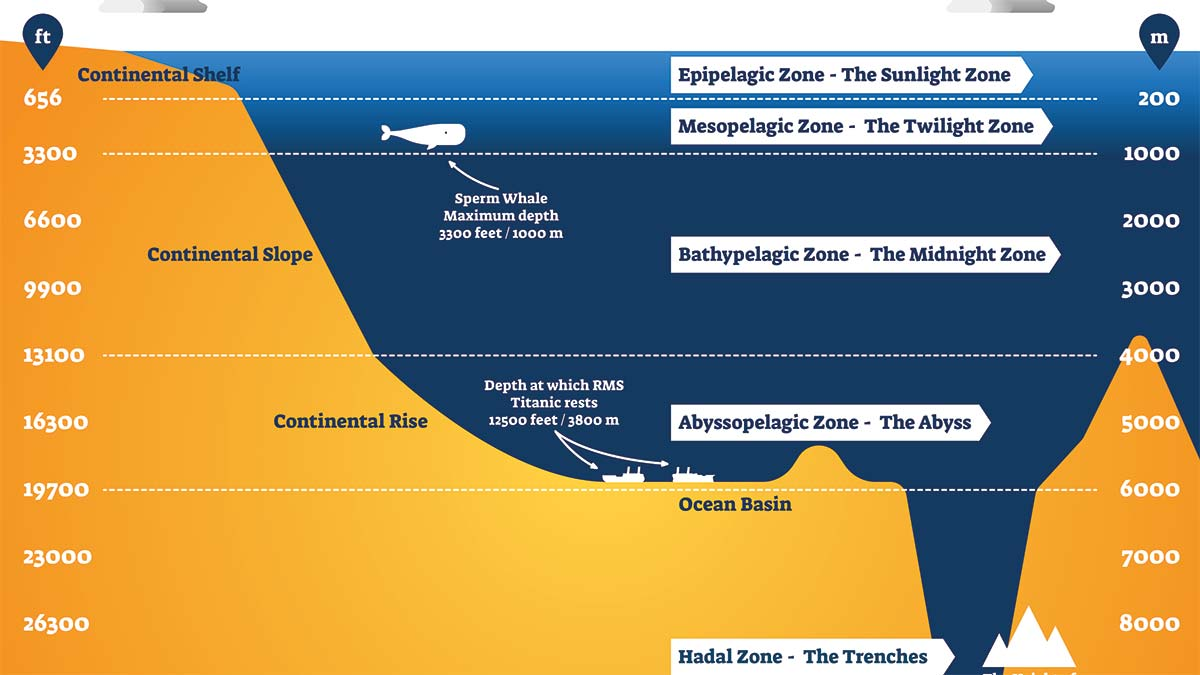
Zones
The ocean is divided into "zones," and these zones exhibit variations in temperature, light availability, and pressure. The distinct zones include the epipelagic, mesopelagic, bathypelagic, abyssopelagic, and hadalagic zones. Each of these zones provides a unique environment for different species, accommodating their specific needs for survival. The epipelagic zone, closest to the ocean's surface, receives more light and is home to a diverse range of species. As we move into the mesopelagic, bathypelagic, and abyssopelagic zones, the conditions change, influencing the types of organisms that inhabit these deeper regions. The hadalagic zone, the deepest part of the ocean, represents the most extreme conditions, both in terms of pressure and darkness.
Pollution
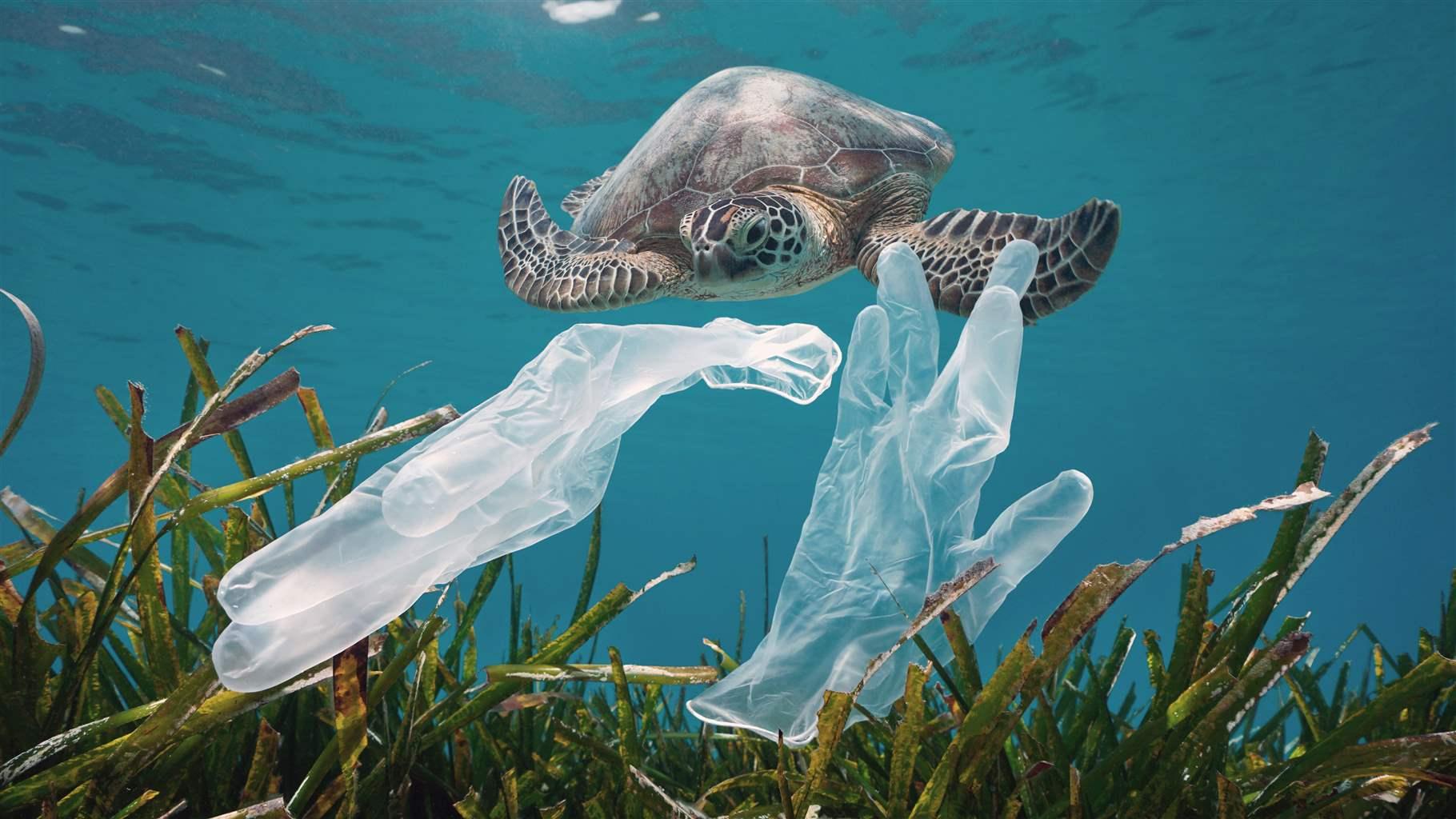
Ocean pollution is when harmful substances or pollutants into the ocean, leading to negative effects on marine life, ecosystems, and ultimately human health. It includes a wide range of pollutants, including plastic debris, chemical contaminants, oil spills, agricultural runoff, and untreated sewage. This pollution can disrupt the ocean's delicate balance, causing harm to marine organisms through ingestion, entanglement, or habitat destruction. Additionally, it can impact human activities such as fishing, tourism, and coastal economies. Efforts to slow down ocean pollution include international agreements, technological innovations, and increased public awareness to reduce, manage, and prevent further damage to the world's oceans.

Go to Works Cited